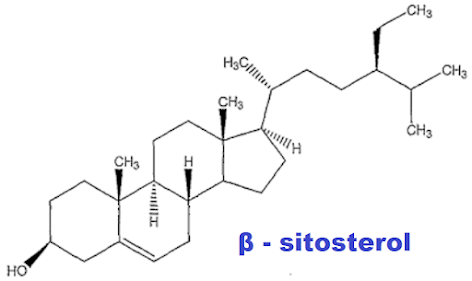
Phytosterols (i.e., plant sterols) are important constituents of plant cells. These compounds are derived from squalene, belonging to the triterpenes family. They are structurally similar to cholesterol, except for the presence of a methyl or ethyl group at the C-24 carbon atom of their side chain.
Phytosterols are important micronutrients structurally similar and functionally analogous to cholesterols. Up to now, more than 250 compounds have been identified. Among the most commonly found phytosterols are β-sitosterol (C-29), campesterol (C-28), and stigmasterol (C-29), which contribute up to 98% of the phytosterol dietary intake in the human diet.
It possesses proven antidiabetic activity. Phytosterols can act as ligands for PPARs (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor), reduce visceral fat accumulation, and reduce the concentration of glycosylated hemoglobin, serum glucose, nitric oxide, and substances that react with thiobarbituric acid, and they can increase serum insulin and pancreatic antioxidants.
The importance of phytosterols is due to their action of reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, and a daily consumption of 2–3 g of phytosterols could decrease the LDL-cholesterol by 10–15%.
Studies have proved the evidence that the phytosterols have a role in protecting against the development of various cancers: ovarian, breast, stomach, prostate and lung cancer. This has been attributed to the effect of phytosterols on membrane structure and function of tumor and host tissue, stopping the growth and spread of cancer cells and encouraging apoptosis.
Vegetable oil, seeds, nuts, and vegetables in general are the major dietary sources of phytosterols. Plant sterols are present in foods in different forms (free, esterified to fatty acids, and linked to glycosides or phenolic acids), and its total content is generally calculated by the sum of all forms.
Banana fruit has been shown to contain a good amount of phytosterols both in the peel and pulp. The phytosterols content in unripe banana in the range of 2.8 to 12.4 g·kg DW has been reported.
Phytosterols isolated from banana flowers (e.g., β-sitosterol and 31-norcyclolaudenone) inhibit amylase as an uncompetitive inhibitor, with a km value of 5.51 μg/mL.
The importance of phytosterols
The primary goal of food is to promote our health and general well-being. Food science entails comprehending the characteristics, composition, and behaviors of food constituents in different situations, such as storage, handling, and consumption.
August 22, 2021
The Most Popular Posts
-
Crude fiber is a measure of the quantity of indigestible cellulose, pentosans, lignin, and other components of this type in present foods. ...
-
Of the many foods obtained from the land, humans tend to prefer animal foods, mainly beef, pork, poultry and mutton as well as their by-pr...
-
Crude fat is the term used to refer to the crude mixture of fat-soluble material present in a sample. Crude fat also known as the ether ext...
-
Gelatinization occurs when starch granules are heated in a liquid. It is responsible for the thickening of food systems. The process is an i...
-
Ash or mineral content is the portion of the food or any organic material that remains after it is burned at very high temperatures. The a...
-
-
-
Most American today are overfed yet undernourished, which eventually leads to obesity and poor health. The answer to those pervasive problem is simply to ...