The pigments are red and yellow and resemble the anthocyanins and flavonoids in an appearance. However the betalains contain nitrogen.
As with anthocyanin, betalains are present in flowers or fruits and may play a role as attractants for vectors in the pollination process and in seeds dispersal by animals.
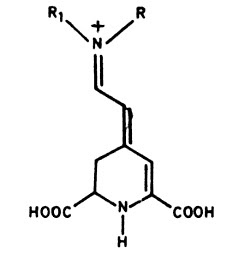 |
| Basic structure of betalains |
Betalains have been proposed as a defense mechanism because they are accumulated when tissues are injured. Moreover, their appearance occurs in association with antifungal proteins in some plants.
The betalains are stable in the pH range 4-6 and they are subject to degradation by thermal processing as in canning.
Within these limitations, betalains are ideally used to color products have a short shelf life, are packaged to reduce exposure to light, oxygen and high humidity, do not received extended or high heat treatment and are marketed in the dry state.
Despite these limitations, betalains have been suggested for coloring ice cream, yoghurt, cake, mixes, gelatin, desserts, meat substitutes, gravies, frostings and many others.
What are betalains?






