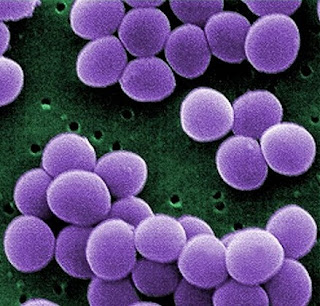
Staphylococcus aureus is a complex bacterial pathogen that is implicated in a wide variety of human and animal infections.
Some Staphylococcus produce a toxin, which is responsible for food poisoning. The staphylococcus enterotoxin is heat stable. The toxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus is not readily destroyed by heat. So that cells of the bacterium can be killed during processing, but the toxin may remain behind.
For this reason, if Staphylococcus aureus is suspected, even if not found, a Staphylococcus toxin test should be performed.
Such foods as milk powder have cause staphylococcus poisoning, yet no living staphylococcus could be isolated from them. In the case of milk powder, the bacteria were destroyed during the heating required for drying the milk.
Almost all strains of S. aureus secrete a group of enzymes and cytotoxins that includes four hemolysins ( α, γ, β, 𝛿), nucleases, proteases, lipases, hyaluronoidase, and collagenase.
Staphylococcus aureus toxin
The primary goal of food is to promote our health and general well-being. Food science entails comprehending the characteristics, composition, and behaviors of food constituents in different situations, such as storage, handling, and consumption.
January 18, 2018
The Most Popular Posts
-
Ash or mineral content is the portion of the food or any organic material that remains after it is burned at very high temperatures. The a...
-
Crude fiber is a measure of the quantity of indigestible cellulose, pentosans, lignin, and other components of this type in present foods. ...
-
Gelatinization occurs when starch granules are heated in a liquid. It is responsible for the thickening of food systems. The process is an i...
-
Crude fat is the term used to refer to the crude mixture of fat-soluble material present in a sample. Crude fat also known as the ether ext...
-
Vegetables are crucial for maintaining good health due to their rich nutrient profile. Historically, plant-based foods have been integral to...
-
-
-
Most American today are overfed yet undernourished, which eventually leads to obesity and poor health. The answer to those pervasive problem is simply to ...